Following a rapid increase at the beginning of 2024, the Ukrainian economy is expected to continue its recovery but at a slower pace due to significant energy shortages. This information is outlined in the National Bank of Ukraine's inflation report for July 2024.
The NBU notes that Ukraine's economy showed strong growth momentum at the beginning of 2024, with real GDP increasing by 6.5% year-on-year in the first quarter, exceeding the NBU's projections. This growth was driven by a stable energy situation, contrasting with the significant energy deficit experienced in January-February 2023. This stability allowed production to expand across various sectors, contributing to high annual growth rates in the energy sector.
Despite a more cautious fiscal policy early in 2024, substantial fiscal impulses from increased budget expenditures in the previous year helped maintain high economic growth in Q1. Specifically, budget expenditures on security and defense, coupled with improved financial results for businesses, spurred investment demand. Construction activities, especially in fortifications and logistics infrastructure, surged, as did housing construction and production of building materials.
Stable maritime corridors and high transitional reserves supported recovery in metallurgy, mining, food processing, and transportation. However, the blockade of western borders limited imports, resulting in a positive contribution of net exports to GDP growth.
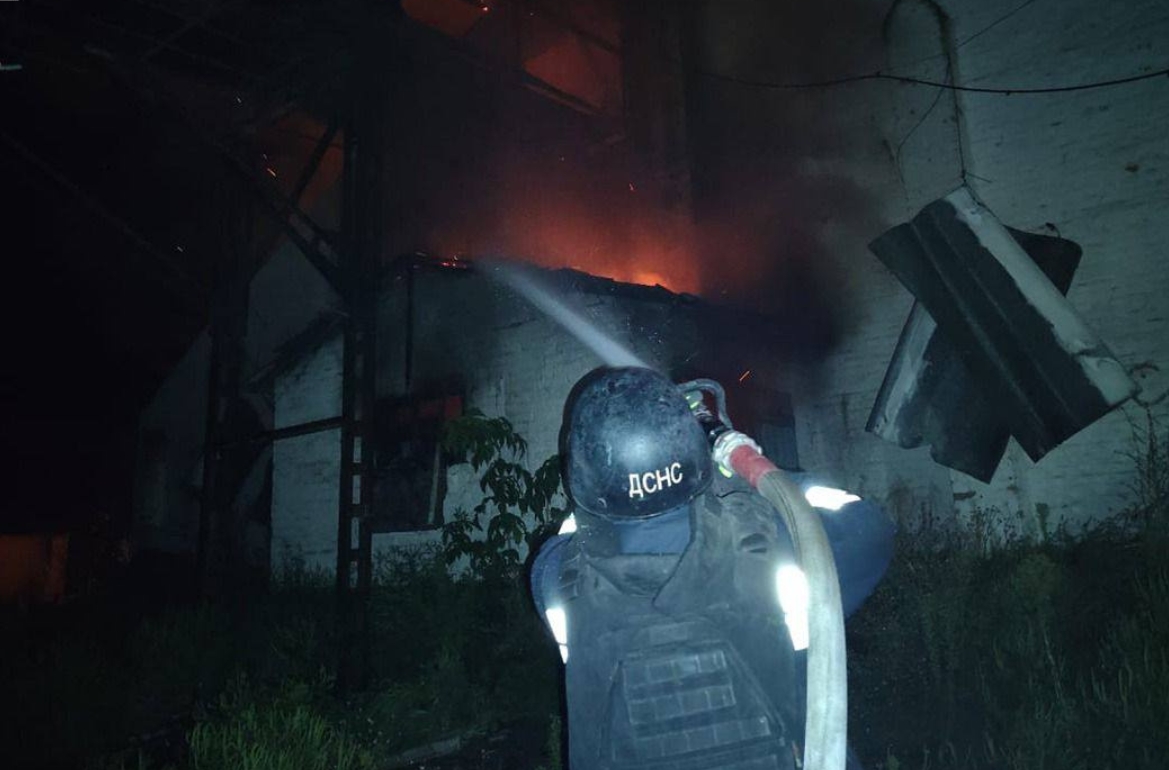
The NBU highlights that the slowdown in growth is primarily due to the destruction of energy infrastructure by Russia and prolonged power outages. Additional energy losses in May-June, coupled with higher energy consumption in summer, have worsened energy deficit forecasts for both Q2 and the outlook period.
Prolonged power outages in Q2 have significantly impacted business and consumer sentiment and weakened economic activity in several sectors, particularly those reliant on energy. Other factors contributing to reduced economic activity include increased staffing issues and longer periods of air alerts.
The NBU forecasts that economic activity will continue to slow in the second half of the year primarily due to higher energy deficits. The shift in the harvest of early grains to June will affect agricultural performance and overall economic activity in Q3. However, better-than-expected results in Q1 2024, improved harvest forecasts due to increased sowing areas, and a larger budget deficit have led to an improved real GDP forecast for 2024 at 3.7%.
Larger energy deficits than previously anticipated will continue to constrain GDP growth throughout the forecast period. A shortage of workers will also limit economic recovery. Nevertheless, with a supportive fiscal policy, increased external demand, and demonstrated adaptability of businesses and the population, the economy is projected to grow by 4-5% in 2025-2026. However, GDP will still remain below its potential level, which will keep inflationary pressures in check, according to the NBU.