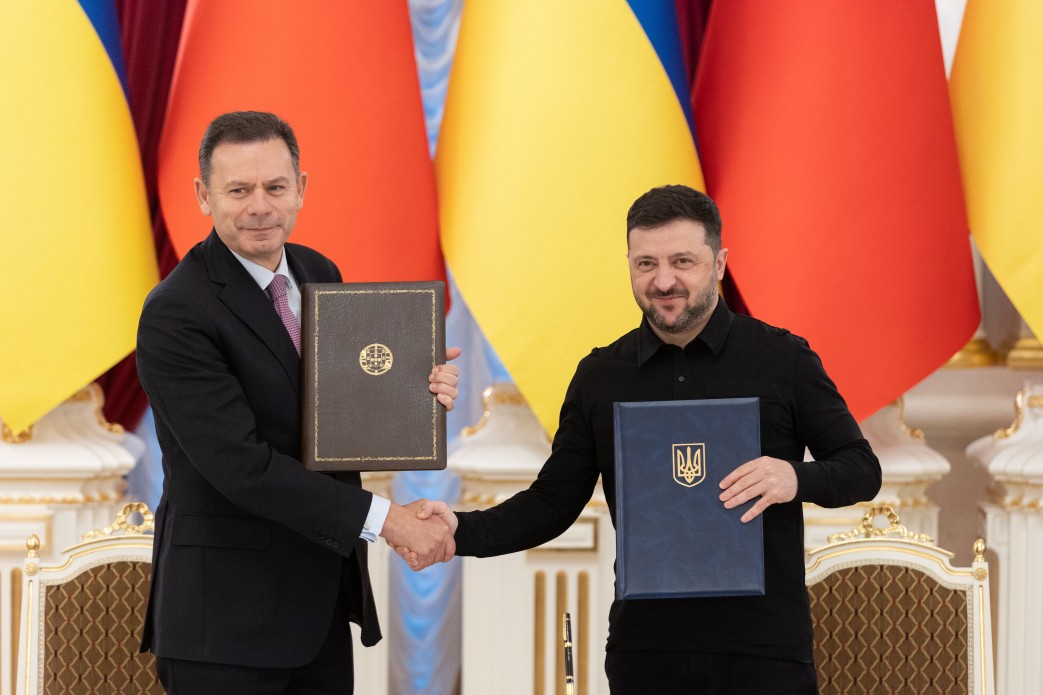
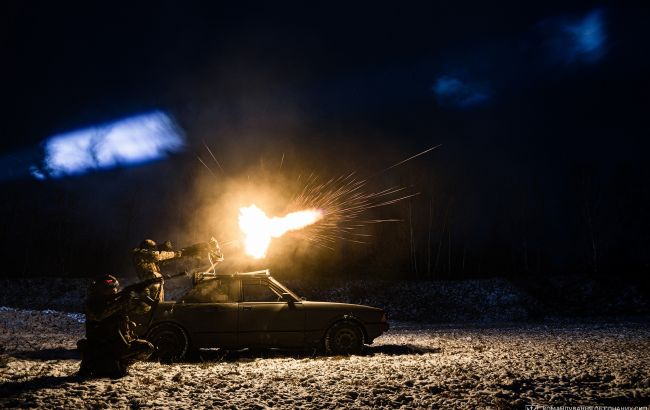
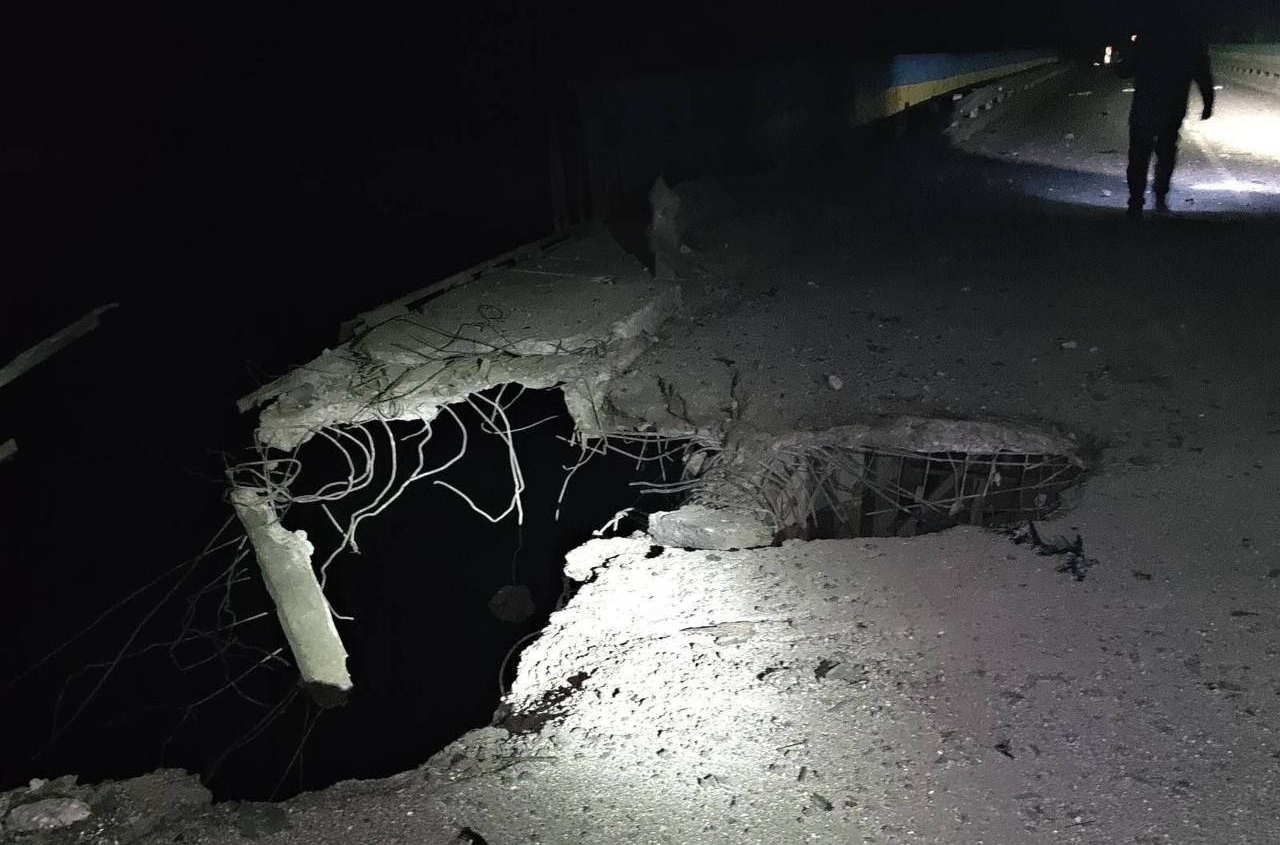
Italy has announced a new package of military aid for Ukraine, which includes the SAMP/T air and missile defense system, 400 M113 armored personnel carriers, artillery ammunition, and satellite support for monitoring the movements of Russian troops.
“We (the EU) have set the amount at 20 billion euros, but I believe we need to exceed this amount. There are also more ambitious commitments to reach 40 billion euros this year. And that is something we can and must do. If everyone allocates 0.25% of their GDP, as we do, then we will easily achieve this financial contribution for Ukraine,” said Latvian Defense Minister Andris Spruds regarding investments in our country’s defense industry, which should provide the ability to negotiate with Russia from a position of strength.
Ukraine and the Czech Republic have agreed to cooperate in training Ukrainian F-16 pilots. The countries will also strengthen their strategic partnership, cooperation in defense industry, economy, and trade. Since the start of the Russian invasion, Ukraine has received aid from the Czech Republic worth 80 million euros for the energy sector.
This year, under the "Czech initiative," Ukraine received 400,000 shells of various calibers.
The International Monetary Fund mission has begun the eighth review of the Extended Fund Facility program with the Ukrainian authorities. Ukraine has already received about 10.1 billion US dollars out of the 15.5 billion US dollars under this program from the IMF.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen believes that reaching a new agreement between Britain and the European Union strengthens support for Ukraine.
“It is important that the United States remain involved in this process. We will continue to support Volodymyr Zelenskyy in achieving lasting peace in Ukraine,” said European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen regarding potential peace negotiations between Russia and Ukraine.
European Commission spokesperson Paola Pinheiro reported that the next negotiations between Ukraine and Russia may already take place with the participation of Europe and the United States.
“They agreed to closely coordinate the negotiation process and strive to hold the next technical meeting... European participants announced increased pressure on the Russian side through sanctions,” the office of German Chancellor Friedrich Merz said in a statement about the results of the phone conversation between US President Donald Trump and Putin.
“Finland continues to support the independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of Ukraine,” assured President Alexander Stubb.
Russia
On May 20, the European Union approved a new sanctions package against Russia, which is the 17th since the full-scale invasion of Ukraine began. According to EU top diplomat Kaja Kallas, the package will affect nearly 200 ships of Russia’s "shadow fleet." "The new measures also address hybrid threats and human rights," Kallas added. The head of European diplomacy also announced the start of work on new sanctions. "The longer Russia wages war, the tougher our response will be," Kallas emphasized.
The EU sanctions target LNG tankers North Moon, North Ocean, and North Light, as well as the dredging vessel Tong Yuan, and two ships for transporting heavy and oversized cargo — Nan Feng Zhi Xing and Ocean 28.
The European Union imposed sanctions on three Russian institutions involved in the development and use of chemical weapons. On the "blacklist" are the troops of radiation, chemical and biological protection, the 27th Scientific Center, and the 33rd Central Research and Testing Institute of the Russian Ministry of Defense.
The EU sanctioned Sergey Kogogin, CEO of PJSC Kamaz. The reason for his inclusion on the sanctions list was the use of Kamaz trucks in the combat zone, as well as the CEO’s support of the military operation on Ukrainian territory.
The EU imposed sanctions on the FGUP "Main Radio Frequency Center," which is subordinate to Roskomnadzor, due to this enterprise’s involvement in GPS disruptions in several European countries, which disrupted civil aviation operations.
The European Union added 28 judges and investigators responsible for human rights violations in Russia to the anti-Russian sanctions list.
The UK government announced an expansion of sanctions against Russia in response to a massive attack on Ukraine on the night of May 18, during which the Russian army used a record number of strike drones. The sanctions will affect 100 entities in Russia’s military, energy, and financial sectors, as well as those conducting an information war against Ukraine.
The EU plans to propose to G7 finance ministers to lower the current price cap on Russian oil transported by sea to 50 dollars per barrel.
Lithuanian Foreign Minister Gintautas Budrys believes that sanctions against Russia’s energy sector can force Putin to cease fire. Budrys thinks the EU should cut off major budget revenues for Russia and its military apparatus, whose source is "exports of gas, oil, and liquefied natural gas."
Despite President Putin’s statements about an “unprecedented” level of partnership with China and “limitless” opportunities for cooperation between the two countries, Chinese investors have sharply reduced their investments in Russia amid the war in Ukraine. While from 2011 to 2018 China invested an average of $1.2 billion annually in Russian projects, in 2022–2023 that figure fell threefold — to $400 million.
Beijing has also significantly reduced its purchases of Russian hydrocarbons. In April, coal and oil supplies dropped by about 13% compared to the same month last year.
Apple was fined 7.5 million rubles in Russia on three counts of “LGBT propaganda.”
Strengthening statehood in Russia should be more important than ensuring citizens’ rights and the rule of law, said Russia’s Minister of Justice Konstantin Chuychenko.
The Deputy Minister of Justice of Russia proposed immediately opening criminal cases for violations of the “foreign agents” law, as currently people “celebrate being included in the registry.”
Russians are finding it increasingly difficult to service debts taken on during the credit boom of 2023 – the first half of 2024. In the first quarter, over 1.5 million people asked banks for loan restructuring — changes to terms or suspension of payments under credit holidays. This is 12% more than in the fourth quarter, and last year the number of restructuring requests grew by 20% each quarter.
From January to April, exports of Chinese passenger cars to Russia fell almost by half, and trucks dropped fivefold, according to data from China’s General Administration of Customs. Thus, the volume of Chinese passenger cars shipped to Russia from January to April fell by 47.2%, and in April alone by 16.2% compared to March 2025. Truck shipments in the first four months of 2025 collapsed fivefold (-79.7%).
Lithuanian President Gitanas Nausėda stated that regional countries might join Lithuania’s lawsuit against Belarus at the UN International Court of Justice in The Hague over the provoked migration crisis. Commenting on the lawsuit, Nausėda emphasized that the Lukashenko regime’s actions violate international law.
The Minsk Wheel Tractor Plant (VAT) was included in the EU Council’s 17th package of sanctions against Russia due to aggression in Ukraine.
Since the protests in Belarus in 2020, over 6,000 people have been convicted, said Dmitry Gora, head of Belarus’s Investigative Committee. Additionally, he noted the liquidation of the Union of Poles in Belarus, whose members, according to him, honored Nazi collaborators (which the committee considers the Polish Home Army from World War II) and “involved youth in criminal actions.” Belarus is also investigating 50 criminal cases “against officials of Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland.” The victims include 349 foreigners, 58 of whom died. The cases concern attempts by migrants to break through from Belarus into European Union countries.
In Malyye Sekhnovichi (Zhabbinksky District, Brest Region), which the Kostyushko family owned for several centuries, the very first monument in Belarus to Tadeusz Kościuszko — a national hero, leader of the 1794 uprising, and a famous native of Belarus honored both in the country and abroad — was demolished. In 2023, Igor Sergienko, head of the Lukashenko administration, stated that he does not consider Tadeusz Kościuszko or Kastus Kalinowski to be national heroes of Belarus. That same year, educational institutions received “recommendations” on how teachers should properly teach history, literature, social studies, and other subjects. By order, students began to be told that Tadeusz Kościuszko was a patriot of Poland whose goal was to restore the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as it existed in 1772, and that for Belarusians, the defeat of Kościuszko’s uprising and the partitions of the Commonwealth allowed them to survive as a people. In April 2024, the memorial plaque honoring Tadeusz Kościuszko, which had hung on the wall of the New Castle in Grodno for 30 years, also disappeared.
In Belarusian children’s camps, instead of Belarusian schoolchildren, the Lukashenko regime plans to provide state-funded health improvement stays for children from Russia, Algeria, and Egypt. There are no places for Belarusian children.
Belarus now has 5 new political prisoners. According to human rights activists, there are currently 1,182 political prisoners in Belarus.